
- #Gnu gcc compiler for code blocks how to
- #Gnu gcc compiler for code blocks download
- #Gnu gcc compiler for code blocks free
- #Gnu gcc compiler for code blocks windows
Single-stepping thru a loop with a large count is time-consuming. The "Continue" resumes the program execution, up to the next breakpoint, or till the end of the program. To set a breakpoint on a particular line, click the left-margin of that line (or select "Toggle Breakpoint (F5)" from "Debug" menu).
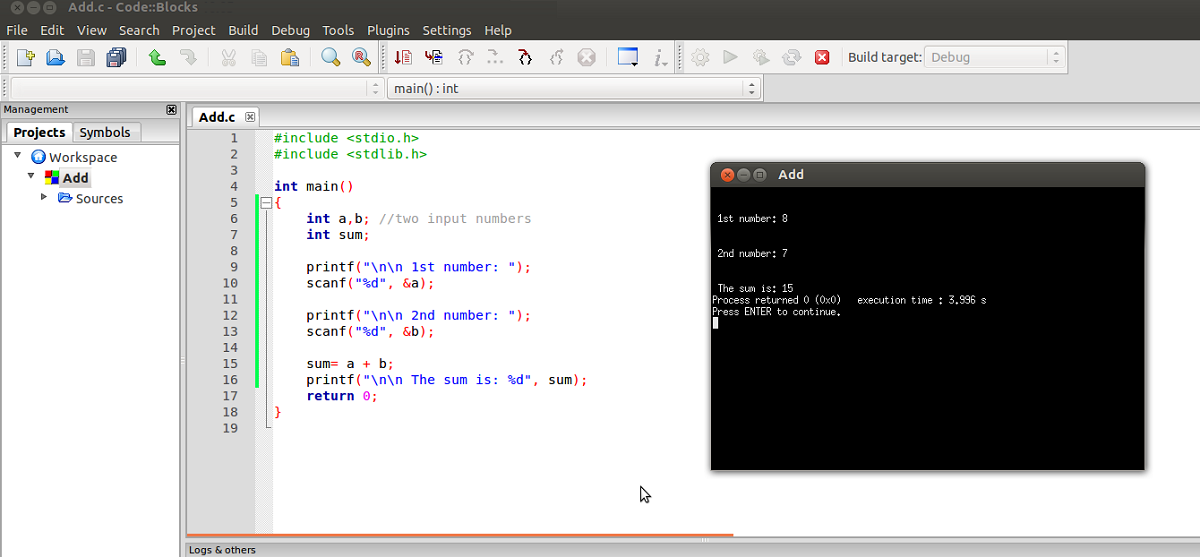
Single-stepping thru the program and watching the values of the variables and the outputs produced is the ultimate mean in debugging programs - because it is exactly how the computer runs your program! Step 4: Breakpoint, Run-To-Cursor, Continue and StopĪs mentioned, a breakpoint suspends program execution and let you examine the internal states of the program. At each of the step, you could examine the internal state of your program, such as the value of the variables (in the "Watches" pane), the outputs produced by your program (in the console), etc. (You could also do it from the "Debug" menu.)Ĭlick the "Next line" button on the "Debug" toolbar to single-step thru your program. Step 3: Single-Step and Watch the Variables and OutputsĬlick the "Debugging Windows" button on the "Debug" toolbar and select "Watches" to enable the "Watch" pane. An yellow arrow (as shown in the diagram) appears and points at the main(), indicating this is the next statement to be executed. The program begins execution but suspends its execution at the breakpoint, i.e., main(). Step 2: Start Debuggingįrom "Debug" menu, select "Start (F8)". A breakpoint suspends program execution for you to examine the internal states. A red circle appears indicating a breakpoint has been set at that line. Set an initial breakpoint at main() function by clicking on the "left-margin" (right-side of the line number) of the line containing main(). Let's use the graphic debugger to debug the program. Run the program and observe the output produced: Int factorial = 1 // Initialize the product to 1Ĭout << "The Factorial of " << n << " is " << factorial << endl
#Gnu gcc compiler for code blocks how to
I resolved by installing the latast MinGW (gcc 4.8.1, gdb 7.6.1) separately (See " How to install MinGW"), and configured the compiler's and debugger's path to the installed MinGW as in the above step.Īlternatively, consider using Eclipse or Netbeans with Cygwin or MinGW GNU GCC compiler. I encountered problem running debugger with CodeBlocks 13.12 bundled with MinGW (gcc v4.7.1 and gdb 7.5).
#Gnu gcc compiler for code blocks windows
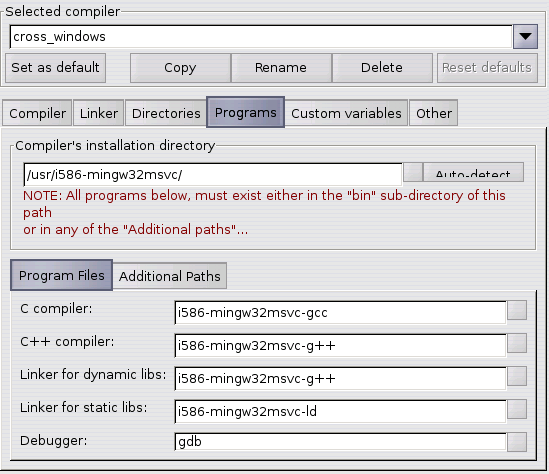
Notes For CodeBlocks 13.12 For Windows (Jan 2014) Goto "Settings" menu ⇒ "Debugger." ⇒ Expand "GDB/CDB debugger" ⇒ Select "Default" ⇒ In "Executable path", provide the full-path name of " gdb.exe", for example, " c:\Program Files\codeblocks\MinGW\bin\gdb.exe". It shall be set to the "MinGW" sub-directory of the CodeBlocks installation directory, for example, suppose that CodeBlocks is installed in " c:\Program Files\codeblocks", set it to " c:\Program Files\codeblocks\MinGW".

Verify the Compiler's and Debugger's Path: (For CodeBlocks 13.12 For Windows) Goto "Settings" menu ⇒ "Compiler." ⇒ In "Selected Compiler", choose "GNU GCC Compiler" ⇒ Select tab "Toolchain Executables" ⇒ Check the "Compiler's Installation Directory".
#Gnu gcc compiler for code blocks download
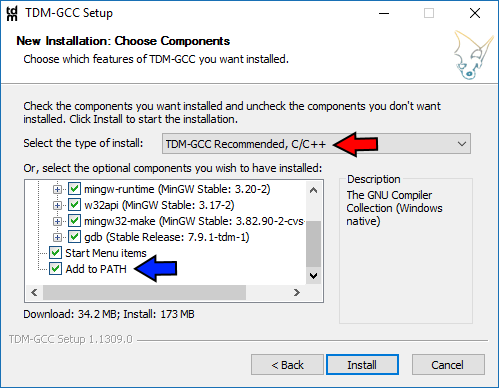
Download the installer with GCC Compiler, e.g., (98 MB) (which includes MinGW's GNU GCC compiler and GNU GDB debugger). Select your operating platform (e.g., Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7). The mother site of CodeBlocks is How to Install CodeBlocks 13.12 Step 1: Download CodeBlocks is surprisingly versatile, and in my opinion, much better than the Visual Studio suite. It supports interactive debugging (via GNU GDB or MS CDB). It supports many compilers, such as GNU GCC (MinGW and Cygwin) and MS Visual C++.
#Gnu gcc compiler for code blocks free
CodeBlocks is an open-source, cross-platform (Windows, Linux, MacOS), and free C/C++ IDE.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
